Understanding Orthopedic Care
Orthopedic care focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disorders related to the musculoskeletal system, including bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. Conditions treated by orthopedic specialists range from fractures and dislocations to degenerative diseases like arthritis and complex congenital deformities.
Key Areas of Orthopedic Care
- Joint Replacement: Procedures such as total hip and knee replacements.
- Trauma Surgery: Treatment of fractures and severe injuries.
- Spinal Surgery: Interventions for conditions like herniated discs and spinal stenosis.
- Sports Medicine: Addressing injuries and conditions common in athletes.
- Pediatric Orthopedics: Treatment of musculoskeletal issues in children.
The Role of Advanced Power Tools in Orthopedic Surgery
Power tools have become indispensable in orthopedic surgery, offering enhanced precision, reduced surgery times, and improved outcomes. These tools are used for various procedures, including cutting, drilling, shaping, and fixing bones and tissues.
Types of Orthopedic Power Tools
- Bone Saws
- Oscillating Saws: Used for precise bone cutting with minimal heat generation.
- Reciprocating Saws: Ideal for cutting through dense bone structures.
- Drills and Reamers
- Cannulated Drills: Allow for accurate drilling through bones, often used in implant placement.
- Powered Reamers: Enlarge or smooth bone cavities, crucial for joint replacement surgeries.
- Screwdrivers and Wrenches
- Electric Screwdrivers: Facilitate the insertion and removal of screws with high precision.
- Torque Wrenches: Ensure screws are tightened to the correct tension, preventing over-tightening.
- Cauterizing Tools
- Electrocautery Devices: Used to control bleeding and remove unwanted tissue during surgery.
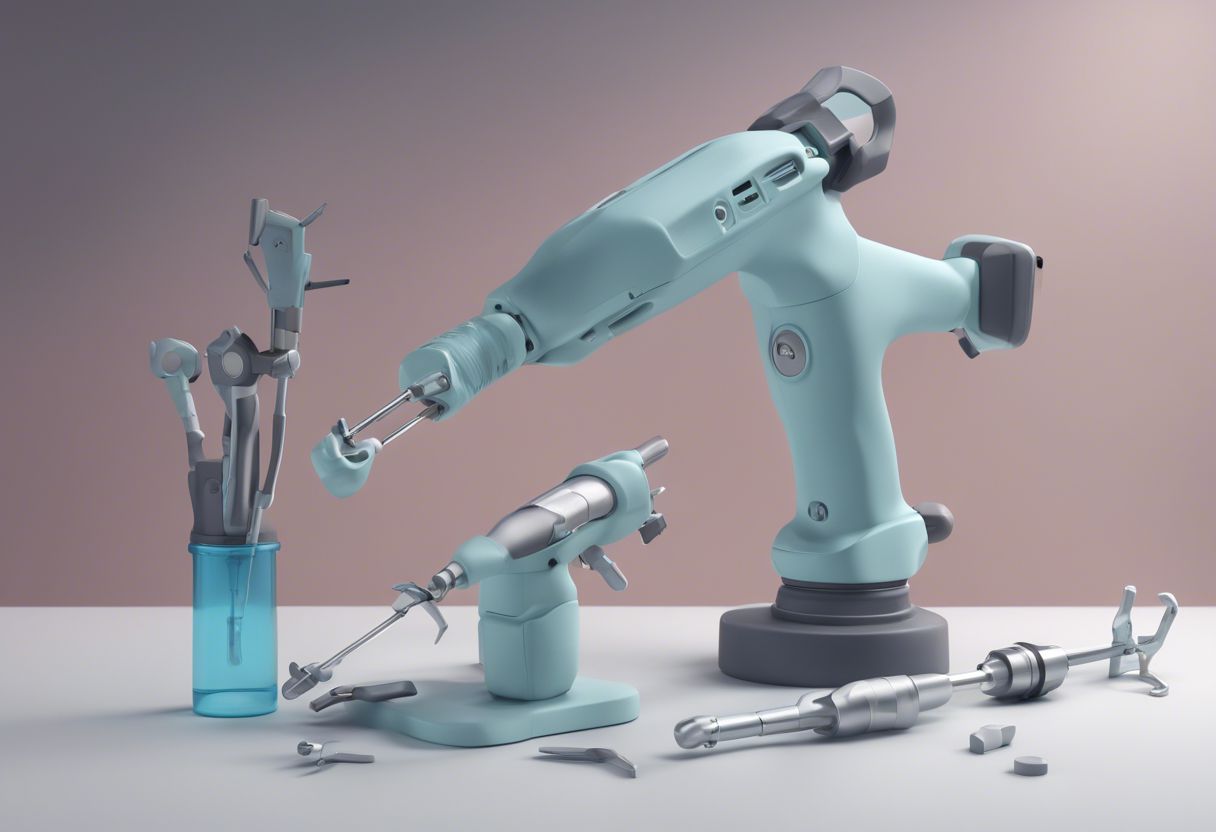
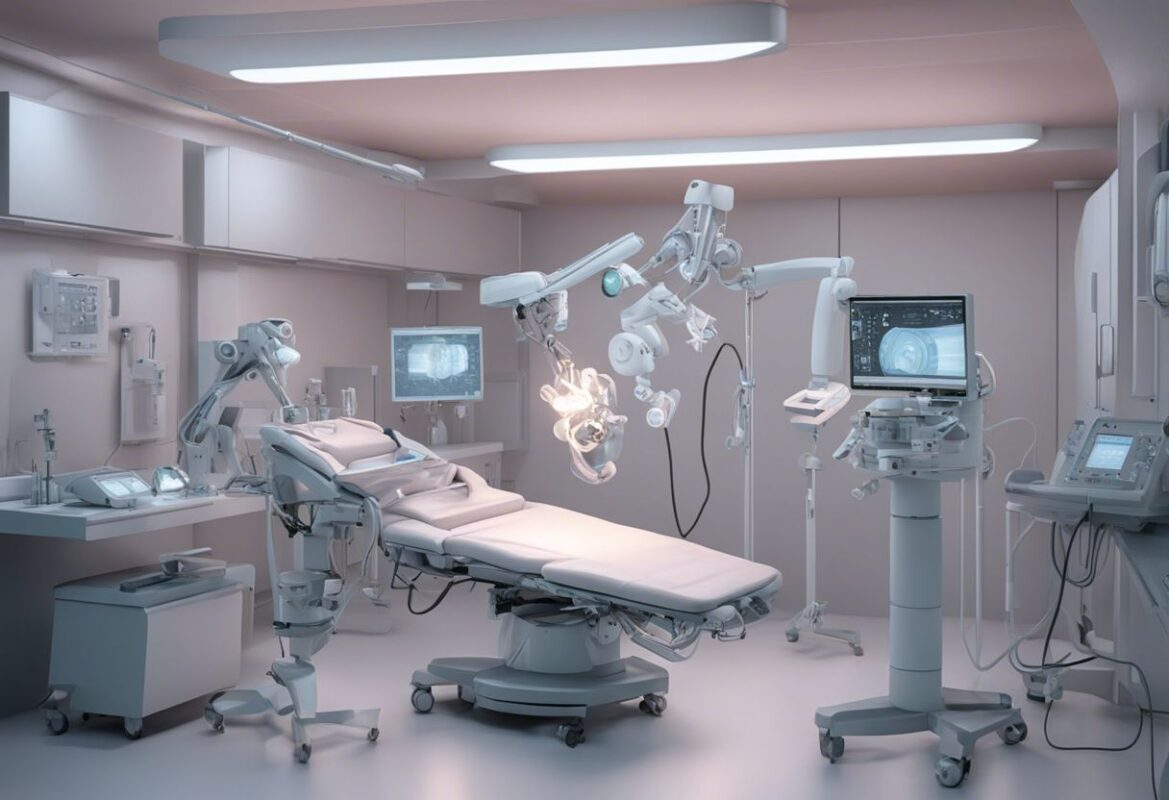
- Robotic-Assisted Tools
- Robotic Arms: Provide enhanced precision and control, allowing for minimally invasive surgeries.
Benefits of Advanced Power Tools
- Precision and Accuracy
- Power tools enable surgeons to perform highly precise cuts and adjustments, essential for successful orthopedic procedures.
- Reduced Surgery Time
- The efficiency of power tools reduces the time required for surgery, minimizing the risk of complications and anesthesia-related issues.
- Enhanced Safety
- Modern power tools are designed with safety features that protect both patients and surgical teams.
- Improved Outcomes
- The precision and efficiency of power tools contribute to better alignment of bones and implants, leading to improved patient outcomes and faster recovery times.
Applications of Power Tools in Orthopedic Surgery
Joint Replacement Surgery
Joint replacement surgeries, such as hip and knee replacements, rely heavily on power tools for cutting and shaping bones to fit implants. Oscillating saws and powered reamers ensure accurate preparation of bone surfaces, which is crucial for the longevity and functionality of the implants.
Trauma Surgery
In trauma surgery, power drills and screwdrivers are used to fix fractures with plates and screws. The precision of these tools is vital for aligning fractured bones correctly, ensuring proper healing and function.
Spinal Surgery
Spinal surgeries often involve delicate procedures where precision is paramount. Powered reamers and drills are used to prepare vertebrae for implants or to decompress nerves, ensuring minimal disruption to surrounding tissues.
Sports Medicine
Arthroscopic tools, which include small power drills and shavers, are used in minimally invasive surgeries for repairing ligaments, tendons, and other soft tissues. These tools allow for quicker recovery times and less post-operative pain.
Pediatric Orthopedics
Power tools in pediatric orthopedics must be adapted for smaller, more delicate bones. Specially designed tools ensure that procedures on young patients are both safe and effective.
Future Trends in Orthopedic Power Tools and Technologies
The field of orthopedic power tools is continuously evolving, with several exciting trends on the horizon.
Robotics and Automation
Robotic-assisted surgery is becoming more prevalent, offering unmatched precision and control. These systems can plan and execute complex procedures with minimal human intervention, reducing the risk of errors and improving patient outcomes.
Advanced Imaging Integration
Integration of advanced imaging technologies, such as 3D imaging and intraoperative CT scans, with power tools allows for real-time visualization and guidance during surgery. This leads to more accurate placements and adjustments.
Smart Tools and IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is making its way into orthopedic surgery, with smart tools that provide real-time feedback on pressure, torque, and other critical parameters. These tools enhance the surgeon’s ability to make precise adjustments during procedures.
Customization and 3D Printing
3D printing technology enables the creation of customized implants and surgical guides tailored to the patient’s anatomy. Power tools designed for use with these custom components ensure perfect fits and improved surgical outcomes.
Enhanced Ergonomics and Design
Future power tools will likely feature improved ergonomics, making them easier to handle and reducing surgeon fatigue. Enhanced designs will also focus on increasing the efficiency and safety of surgical procedures.
Conclusion
The integration of advanced power tools into orthopedic surgery has significantly improved the precision, safety, and outcomes of various procedures. As technology continues to advance, the future of orthopedic care looks promising, with innovations that will further enhance the capabilities of surgeons and the quality of patient care. By staying informed about these developments, your med-tech distribution business can position itself at the forefront of this dynamic and rapidly evolving field, offering cutting-edge solutions that meet the needs of healthcare providers and their patients.