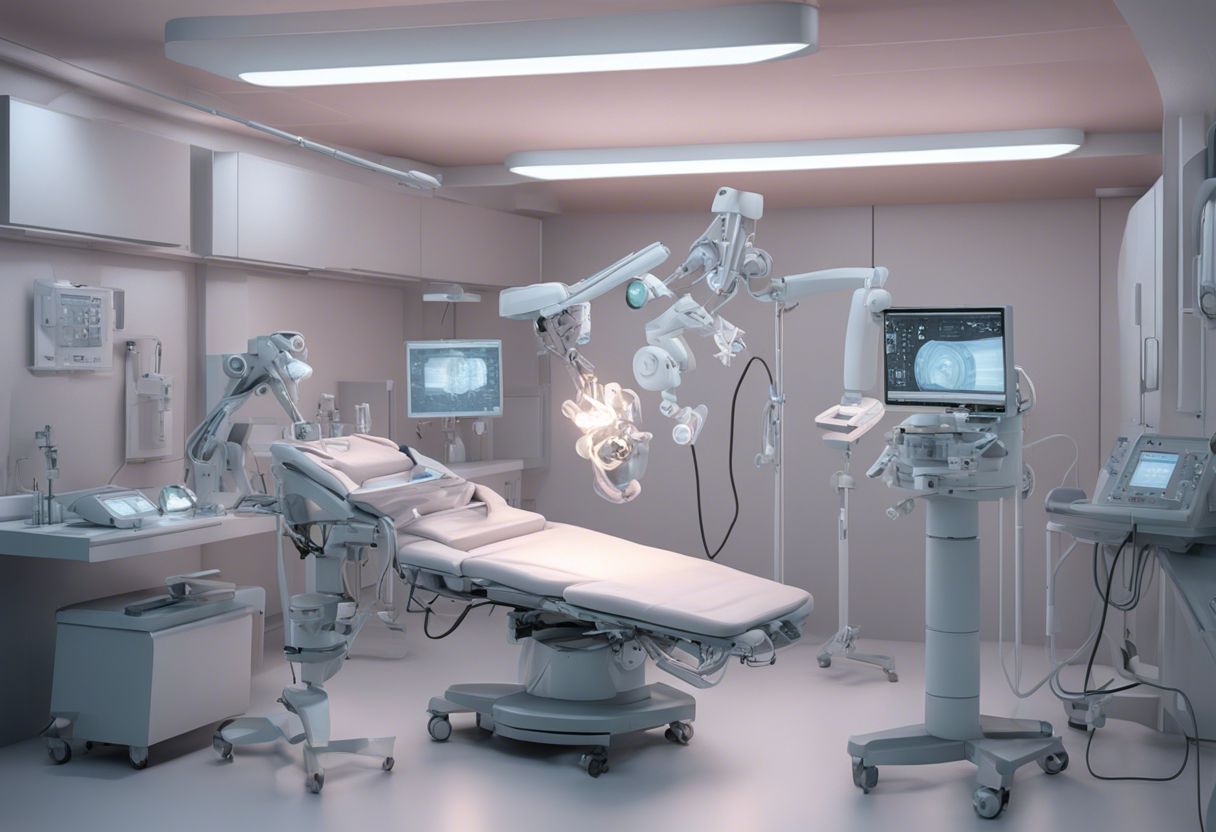
Surgical robotics has emerged as one of the most transformative advancements in medical technology, revolutionizing the way surgeries are performed. By enhancing precision, reducing invasiveness, and improving patient outcomes, robotic-assisted surgery represents the future of surgical care. In this comprehensive post, we explore the various types of surgical robots, their applications, and the future trends driving this cutting-edge field.
Understanding Surgical Robotics
Surgical robots are sophisticated systems designed to assist surgeons in performing complex procedures with enhanced precision and control. These robots can replicate and enhance the surgeon’s movements, providing superior dexterity and accuracy.
Key Characteristics of Surgical Robots
- Precision: Ability to perform highly intricate and delicate maneuvers with minimal error.
- Minimally Invasive: Enables surgeries through small incisions, reducing trauma and recovery time.
- Enhanced Visualization: Provides high-definition, 3D views of the surgical field.
- Improved Dexterity: Robotic instruments offer a greater range of motion than the human hand.
Types of Surgical Robots and Their Applications
1. Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Surgery
Overview
Robotic-assisted laparoscopic systems are used for minimally invasive surgeries, enhancing the surgeon’s capabilities through tiny incisions.
Systems
- Da Vinci Surgical System: The most widely used platform for a variety of laparoscopic procedures.
- Senhance Surgical System: Provides haptic feedback and eye-tracking camera control.
Applications
- General surgery (e.g., cholecystectomy, appendectomy)
- Gynecological surgery (e.g., hysterectomy, myomectomy)
- Urological surgery (e.g., prostatectomy, nephrectomy)
- Thoracic surgery (e.g., lung resection)
2. Orthopedic Robotic Surgery
Overview
Orthopedic robots assist in precise bone cutting and placement of implants, crucial for successful joint replacement surgeries.
Systems
- MAKOplasty: Specializes in partial knee and total hip replacements, providing real-time data and enhanced accuracy.
- ROBODOC: Used for total hip and knee arthroplasty, offering precise bone preparation.
Applications
- Total hip replacement
- Total and partial knee replacement
- Spine surgery
- Trauma surgery
3. Neurosurgical Robots
Overview
Neurosurgical robots provide high precision for delicate brain and spinal procedures, reducing the risk of damage to critical structures.
Systems
- ROSA (Robotic Surgical Assistant): Used for stereotactic neurosurgery, epilepsy surgery, and brain biopsies.
- Neuromate: Assists in various cranial procedures, offering precise positioning.
Applications
- Deep brain stimulation (DBS)
- Stereotactic biopsies
- Tumor resection
- Epilepsy surgery
4. Cardiac Robotic Surgery
Overview
Cardiac robots facilitate minimally invasive heart surgeries, reducing recovery times and improving outcomes.
Systems
- Da Vinci Surgical System: Also used for various cardiac procedures, providing precision and control.
- CorPath GRX: Specializes in percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI).
Applications
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
- Mitral valve repair
- Atrial septal defect (ASD) closure
- Percutaneous coronary interventions
5. Robotic Catheters
Overview
Robotic catheter systems are used in interventional cardiology and radiology, enhancing the precision of catheter navigation.
Systems
- Sensei X Robotic Catheter System: Provides precise control for complex ablations.
- Magellan Robotic System: Used for peripheral vascular interventions.
Applications
- Cardiac ablation procedures
- Vascular interventions
- Endovascular aneurysm repair
- Electrophysiology studies
Benefits of Surgical Robotics
Enhanced Precision and Control
Surgical robots translate the surgeon’s movements into precise actions, significantly reducing the margin of error. This precision is crucial for complex procedures involving delicate tissues and structures.
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Robotic systems enable minimally invasive surgeries through small incisions, resulting in less trauma, reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times for patients.
Superior Visualization
High-definition, 3D visualization provided by robotic systems allows surgeons to see the surgical field with greater clarity and depth, improving their ability to perform complex tasks.
Increased Dexterity
Robotic instruments offer greater dexterity and a wider range of motion than the human hand, allowing for more intricate and precise maneuvers during surgery.
Consistency and Reduced Fatigue
Robots can perform repetitive tasks with consistent precision, reducing surgeon fatigue and improving the overall quality of surgery, especially during long and complex procedures.
Future Trends in Surgical Robotics
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Innovation: Integration of AI and machine learning to enhance surgical planning, real-time decision-making, and outcome prediction.
- Impact: Improved accuracy, personalized surgical approaches, and reduced intraoperative risks.
Advanced Imaging Integration
- Innovation: Incorporation of advanced imaging technologies like augmented reality (AR) and real-time 3D imaging into surgical robots.
- Impact: Enhanced visualization, better navigation, and improved surgical outcomes.
Tele-Surgery and Remote Operations
- Innovation: Development of tele-surgery capabilities, allowing surgeons to perform operations remotely using robotic systems.
- Impact: Increased access to expert surgical care, especially in underserved and remote areas.
Enhanced Haptic Feedback
- Innovation: Improved haptic feedback systems to provide surgeons with tactile sensations during robotic surgery.
- Impact: Better control and precision, reducing the risk of inadvertent tissue damage.
Cost Reduction and Accessibility
- Innovation: Advances in technology and manufacturing are driving down the costs of surgical robots.
- Impact: Increased accessibility and adoption of robotic surgery across various healthcare settings, including smaller hospitals and clinics.
Conclusion
Surgical robotics represents a monumental leap forward in the field of surgery, offering unparalleled precision, control, and patient outcomes. From minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures to complex neurosurgical and orthopedic interventions, robotic systems are transforming the surgical landscape. As technology continues to advance, the future of surgical robotics promises even greater innovations, including AI integration, enhanced imaging, and remote surgery capabilities. By staying at the forefront of these developments, healthcare providers can offer cutting-edge surgical care, ensuring the highest standards of patient safety and outcomes.