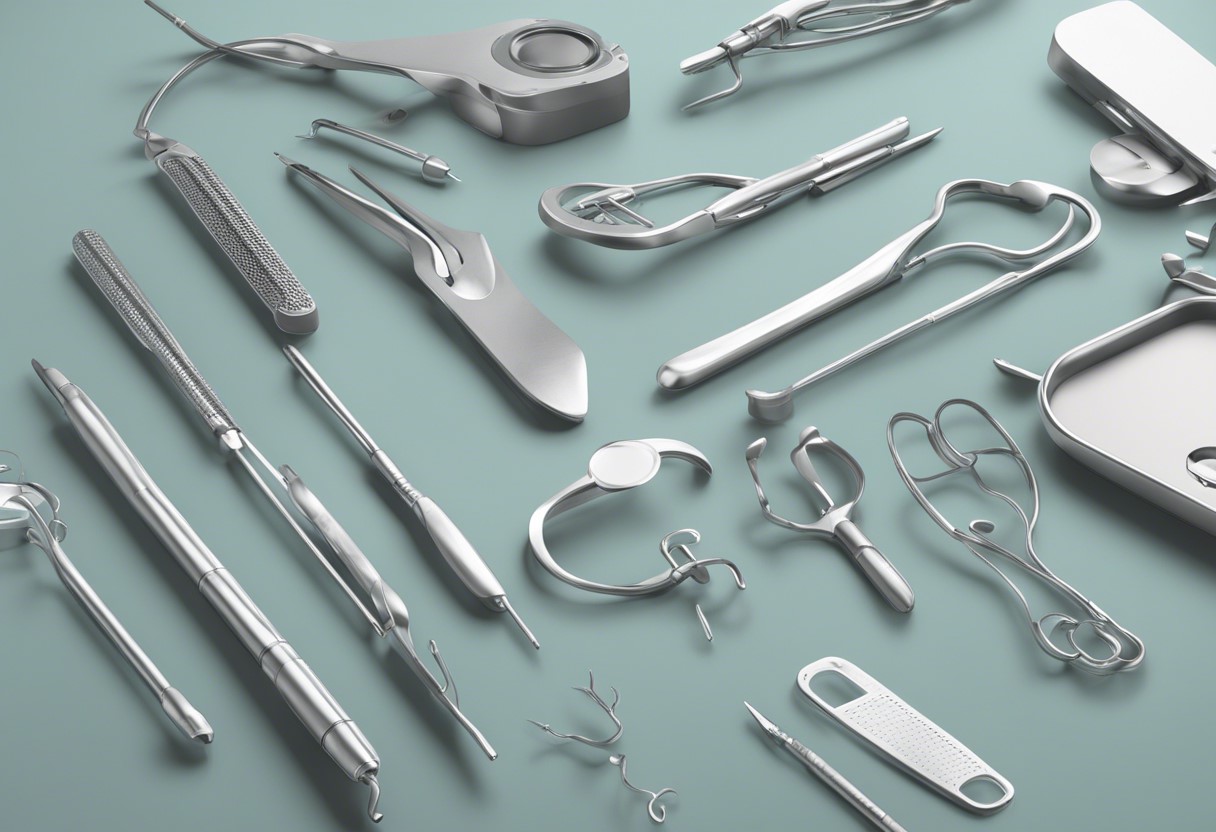
Stainless steel has long been the material of choice for manufacturing medical instruments due to its exceptional properties, including corrosion resistance, durability, and biocompatibility. Various types of core stainless steels are used in medical instruments, each offering distinct advantages tailored to specific applications. In this detailed post, we explore the different types of core stainless steels, their properties, and their applications in the medical field.
Understanding Stainless Steel in Medical Instruments
Stainless steel is an alloy primarily composed of iron, chromium, and other elements such as nickel, molybdenum, and carbon. The addition of chromium provides a passive layer of chromium oxide on the surface, which prevents corrosion and enhances durability. Depending on the specific alloy composition and processing methods, stainless steel can exhibit a wide range of properties suitable for various medical applications.
Types of Core Stainless Steels Used in Medical Instruments
1. Austenitic Stainless Steel
Austenitic stainless steel is known for its high corrosion resistance, excellent formability, and good mechanical properties. The most common grades used in medical instruments include 304 and 316.
Grade 304
- Composition: Contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel.
- Properties: Highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation, easy to clean, and non-magnetic.
- Applications: Surgical instruments, needles, catheters, and dental tools.
Grade 316
- Composition: Contains 16-18% chromium, 10-14% nickel, and 2-3% molybdenum.
- Properties: Enhanced corrosion resistance, particularly against chlorides, making it suitable for more demanding environments.
- Applications: Implants, surgical instruments exposed to saline environments, and orthopedic devices.
2. Martensitic Stainless Steel
Martensitic stainless steel is characterized by its high strength and hardness, achieved through heat treatment. Common grades used in medical instruments include 410, 420, and 440.
Grade 410
- Composition: Contains 11.5-13.5% chromium.
- Properties: Good hardness and moderate corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Surgical scissors, forceps, and retractors.
Grade 420
- Composition: Contains 12-14% chromium with higher carbon content than 410.
- Properties: Higher hardness and strength, excellent polishability.
- Applications: Surgical blades, scalpels, and dental instruments.
Grade 440
- Composition: Contains 16-18% chromium and higher carbon content for increased hardness.
- Properties: Exceptional hardness and wear resistance, used for cutting instruments.
- Applications: High-quality surgical blades, chisels, and orthopedic tools.
3. Duplex Stainless Steel
Duplex stainless steel combines the best properties of austenitic and ferritic stainless steels, offering high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. Commonly used grades include 2205 and 2507.
Grade 2205
- Composition: Contains 22% chromium, 5-6% nickel, and 3% molybdenum.
- Properties: Superior resistance to stress corrosion cracking and high mechanical strength.
- Applications: Surgical instruments requiring high durability, medical device components.
Grade 2507
- Composition: Contains 25% chromium, 7% nickel, and 4% molybdenum.
- Properties: Enhanced resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, high strength.
- Applications: Implants, surgical tools used in highly corrosive environments.
4. Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steel
Precipitation-hardening stainless steels offer high strength and hardness through a heat treatment process that precipitates particles within the metal matrix. Common grades include 17-4 PH and 15-5 PH.
Grade 17-4 PH
- Composition: Contains 17% chromium and 4% nickel, with copper and niobium additions.
- Properties: High strength, good corrosion resistance, and excellent fatigue properties.
- Applications: Surgical instruments, dental tools, orthopedic devices.
Grade 15-5 PH
- Composition: Similar to 17-4 PH but with slightly different alloying elements.
- Properties: High strength and toughness, improved corrosion resistance.
- Applications: High-performance surgical instruments, precision medical components.
Advantages of Stainless Steel in Medical Instruments
1. Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel’s inherent resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for medical environments, where instruments are frequently exposed to bodily fluids, sterilization processes, and harsh cleaning agents.
2. Durability and Strength
The high tensile strength and durability of stainless steel ensure that medical instruments can withstand repeated use and sterilization without degrading.
3. Biocompatibility
Stainless steel is biocompatible, meaning it does not cause adverse reactions when in contact with body tissues, making it suitable for implants and other medical devices.
4. Ease of Sterilization
The smooth, non-porous surface of stainless steel instruments is easy to clean and sterilize, reducing the risk of infection.
5. Precision and Versatility
Stainless steel can be precisely machined and shaped into complex designs, allowing for the creation of a wide variety of medical instruments with high precision.
Future Trends in Stainless Steel Medical Instruments
The development of new stainless steel alloys and advanced manufacturing techniques continues to enhance the performance and capabilities of medical instruments. Key trends include:
Nanostructured Stainless Steels
- Innovation: Nanotechnology is being used to develop stainless steel with enhanced mechanical properties and antibacterial surfaces.
- Impact: Reduced infection rates and improved instrument longevity.
Additive Manufacturing
- Innovation: 3D printing with stainless steel alloys allows for the production of customized and complex medical instruments.
- Impact: Personalized medical solutions and faster production times.
Coatings and Surface Treatments
- Innovation: Advanced coatings and surface treatments improve the wear resistance and antibacterial properties of stainless steel instruments.
- Impact: Enhanced performance and reduced risk of contamination.
Conclusion
Stainless steel remains a cornerstone material in the manufacturing of medical instruments, offering unmatched properties that meet the stringent demands of the medical field. By understanding the different types of core stainless steels and their specific applications, manufacturers and healthcare providers can ensure the highest standards of quality and performance. As technology advances, the development of innovative stainless steel alloys and manufacturing techniques will continue to drive improvements in medical instrument design, ultimately enhancing patient care and outcomes.